This post aims to communicate a simple yet powerful idea: if you have a system of coupled oscillators controlled by a coupling kernel, you can use it to not only “tune into resonant modes” of the system, but also as a point of leverage to control the topological structure of the fields interacting with the oscillators.
This might be a way to explain how topological boundaries are mediated by neuronal activity, which in turn can be modulated by drugs/neurotransmitter concentrations, and in this way provide a link between neurochemistry and the topological structure of experience. Two things fall out of this: First, we might have the conceptual tools to link the creation of global topological boundaries (which at QRI we postulate are what separates a moment of experience from the rest of the universe) and neural activity. And second, in turn, we might have the ability to explain as well the way changes in oscillator/neural activity give rise to differently internally structured topologies (which together with a way of interpreting the mapping between topology of a field and its phenomenology) can help us explain things like the phenomenological differences between states of consciousness triggered by the ingestion of drugs as different as DMT and 5-MeO-DMT. In other words, this post is pointing at how we can get topological structure out of oscillatory activity – and thus explain how conscious boundaries (both local and global) are modulated both natively and through neuropharmacological interventions. It’s an algorithmic reduction with potentially very large explanatory power in the realm of consciousness research that only now is becoming conceptually accessible thanks to years of research and development at QRI.
Let’s start with a Big Picture Summary of the framework:
QRI aims to develop a holistic theoretical framework for consciousness. This latest iteration aims to integrate electromagnetic field theories of consciousness, connectome-specific harmonic waves, coupling kernels, and field topology in a way that might be capable of providing both explanatory and predictive power in the realm of phenomenology and its connection to biology. While this is an evolving framework, I see a lot of value in sharing the general idea (the “big picture”) we have at the moment to start informing the community and collaborators about how we’re thinking about unifying frameworks for understanding consciousness at the moment. The core elements of the Big Picture are:
- Coupling Kernels as Neural-Global Bridge: The coupling kernel serves as a critical bridge between local neural circuitry and global brain-wide behavior. As demonstrated in Marco Aqil’s work, when scaling up from neural microcircuits, the power distribution across different system harmonics can be modulated through coupling kernel parameters. This is something we arrived at independently last year in a very empirical and hands-on way, but Marco’s precise mathematical framework provides a solid theoretical foundation for this connection.
- Geometric Constraints on Coupling Effects: The underlying geometry of a system fundamentally shapes how coupling kernels manifest their effects: resonant modes accessible through coupling kernels differ significantly between scale-free and geometric networks. Within geometric networks, specific geometries and dimensionalities generate characteristic resonant patterns. Thus, a single “high level” effect like a change in coupling kernel can have a wide range of different effects depending on the type of network/system to which it is applied.
- Network Geometry Interactions and Projective Intelligence: A fundamental computational principle emerges from the interaction between networks of different geometries/topologies. This underlies “projective intelligence” (or more broadly, mapping/functional intelligence) – as exemplified by the interaction between the 2D visual field and 3D somatic field.
- Topological Solution to the Boundary Problem: The topological solution to the boundary problem elucidates how physically “hard” boundaries with causal significance and holistic behavior could explain the segmentation of consciousness into discrete experiential moments.
- Internal Topology and Phenomenology: The internal topological complexity within a globally segmented topological field pocket may determine its phenomenology – specifically, the field’s topological defects might establish the boundary conditions.
- 5-MeO-DMT and Topological Simplification: 5-MeO-DMT experiences demonstrate phenomenological topological simplification as documented by Cube Flipper and other HEART members.
- Coupling Kernels and Field Topology: Coupling kernels applied to electric oscillators can modulate field topology (observable in the vortices and anti-vortices of the magnetic field containing the electric oscillators, which you can see in the simulations below).
- DMT vs 5-MeO-DMT Effects: This framework offers an explanation for the characteristic effects of DMT and 5-MeO-DMT: DMT generates competing coherence clusters and multiple simultaneous observer perspectives – interpretable as topological complexification within the pocket. Conversely, 5-MeO-DMT induces simplification where boundaries mutually cancel, ultimately producing experiences characterized by a single large pinwheel and the dissolution of topological defects (as in cessation states).
- Paths and Experience: The Path Integral of Perspectives – The final theoretical component suggests that the subjective experience of a topological pocket emerges from “the superposition of all possible paths” within it. The topological simplicity of 5-MeO-DMT states may generate an “all things at once” quality due to the absence of internal boundaries constraining the state. In contrast, DMT’s complex internal topology results in each topological defect functioning as an observer, creating the sensation of multiple entities.
We’re currently developing empirical paradigms to test these frameworks, including psychophysics studies and simulations of brain activity to reconstruct behavior observed through neuroimaging. These ideas are fresh and need a lot of work to be validated and integrated into mainstream science, but we see a path forward and we’re excited to get there.
Now let’s dive into these components and explain them more fully:
0. What’s a Coupling Kernel?
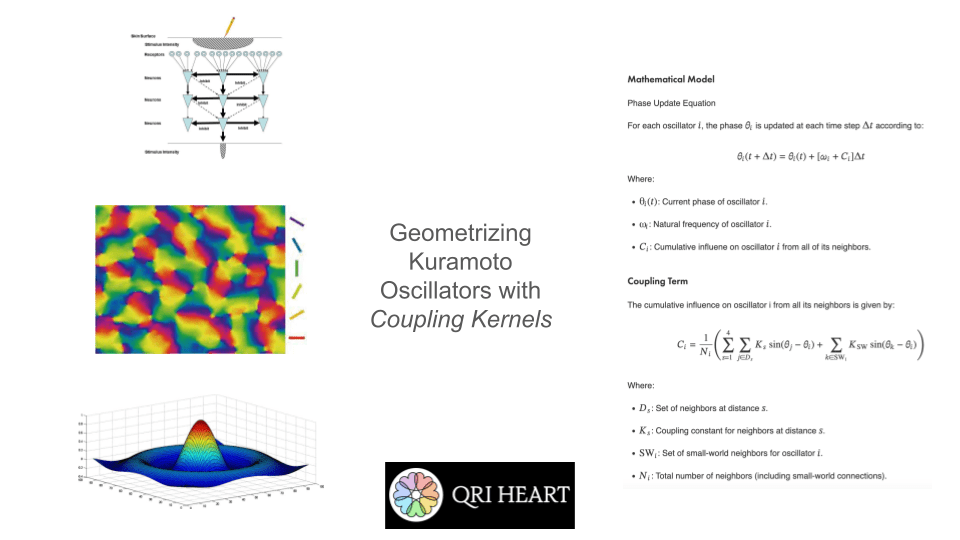
The core concept vis-à-vis QRI was introduced in Cessation states: Computer simulations, phenomenological assessments, and EMF theories (Percy, Gómez-Emilsson, & Fakhri, 2024), where we provided a novel conceptual framework to make sense of meditative cessations (i.e. brief moments at high levels of concentration where “everything disappears”). Coupling kernels was part of the conceptual machinery that allowed us to propose a model for cessations, but it is worth mentioning that it stands on its own as a neat tool that bridges low-level connectivity and high-level resonance in systems of coupled oscillators. The core concept is: in a system of coupled oscillators with a distance function for each pair of oscillators, a coupling kernel is a set of parameters that tells you what the coupling coefficient should be as a function of this distance. I independently arrived at this idea (which others have explored in the past to an extent) during the Canada HEART retreat in order to explain a wide range of phenomenological observations derived from meditative and psychedelic states of consciousness. In particular, we wanted to have a simple algorithmic reduction to be able to explain the divergent effects of DMT and 5-MeO-DMT: the former seems to trigger “competing clusters of coherence” in sensory fields, whereas the latter seems to pull the entire system to a state of global coherence (in a dose-dependent way). Thinking of systems of coupled oscillators, I hypothesized that perhaps DMT induces a sort of alternative coupling kernel (where immediate neighbors want to be as different as possible from each other, whereas neighbors a little further apart want to be similar) while 5-MeO-DMT might instantiate a general “positive kernel” where oscillators all want to be in phase regardless of relative distance. We are in the process of developing empirical paradigms to validate this framework, so please take this with a grain of salt; the paradigm is currently in early developmental stages, but it is nonetheless worth sharing for the reasons I mentioned already (bringing collaborators up to speed and getting the community to start thinking in this new way).
As demonstrated in our work “Towards Computational Simulations of Cessation“, see how a flat “coupling kernel” triggers a global attractor of coherence across the entire system, whereas an alternating negative-positive (Mexican hat-like) kernel produces competing clusters of coherence. This is just a very high-level and abstract demonstration of a change in the dynamic behavior of coupled oscillators by applying a coupling kernel. What we then must do is to see how such a change would impact different systems in the organism as a whole.
Source
It is worth mentioning that in all of our simulations we also add a “small world” lever. The way this one is constructed is as follows: at the start of the simulation, for each oscillator we select two other oscillators at random and wire them to it. The lever controls the coupling constant between each oscillator and the two randomly chosen oscillators assigned to it. In graph theory, this kind of network architecture is often called a “small-world network” because the diameter of the graph quickly collapses as you add more random connections (and in our case, the system synchronizes as you add a positive coupling constant in for these connections). In practice, while the distance-based coupling kernel tunes into resonant modes (traveling waves, checkerboard patterns, etc. as we will see below), the small-world coupling constant adds a kind of geometric noise (when negative) and a global phase to which all oscillators can easily synchronize to (when positive). In effect, we suspect that small-world network-like neural wiring might be responsible for things like dysphoric seizures (due to high level of synchrony coupled with geometric irregularity causing intense dissonance) and disruption of consonant traveling waves (e.g. as a way to modulate anxiety). The phenomenology of being hungover or of experiencing benzo withdrawal might have something to do with an overactive negative small world network coupling constant.
1. Coupling Kernels as Neural-Global Bridge
One of the early simulations that I coded would analyze in real time the Discrete Cosine Transform that the effect of coupling kernels have on a 2D system of oscillators. Intuitively, I knew that the shape of the kernel clearly selected for specific resonant modes of the entire system, but seeing in real time how robust this effect was made me think there probably was a deep mathematical reason behind it. Indeed, as you can see in the below animations, the kernel shape can select checkerboard patterns, traveling waves, and even large pinwheels, all of which have characteristic spatial frequencies that are easily noted in the DCT of the plate of oscillators.
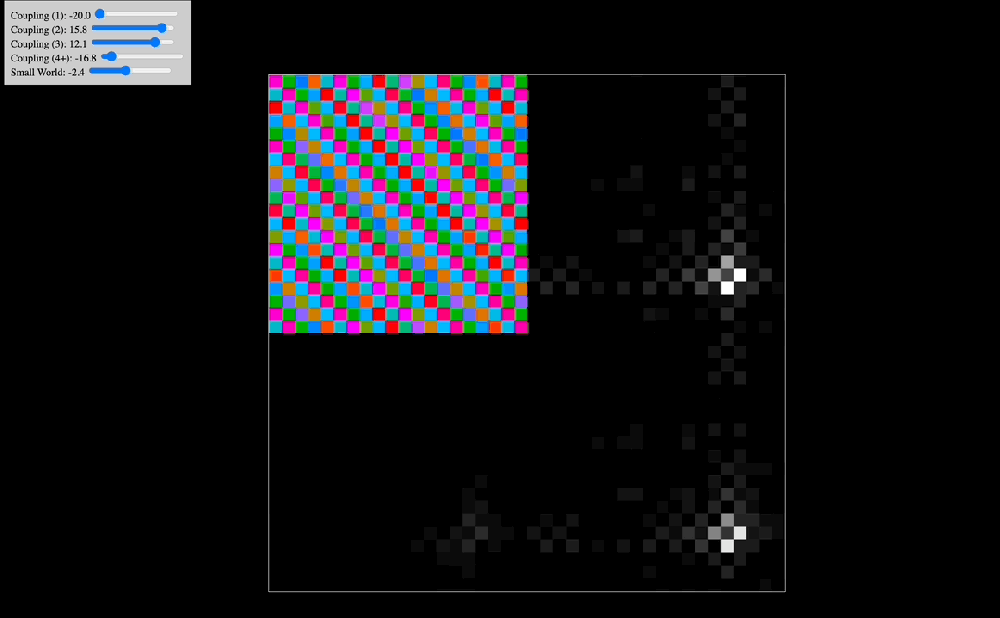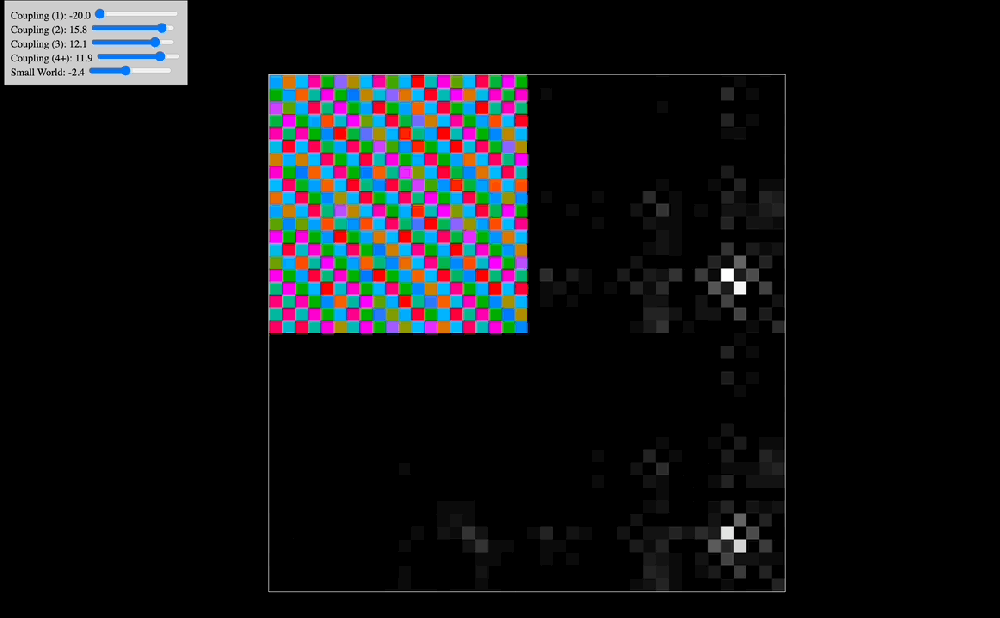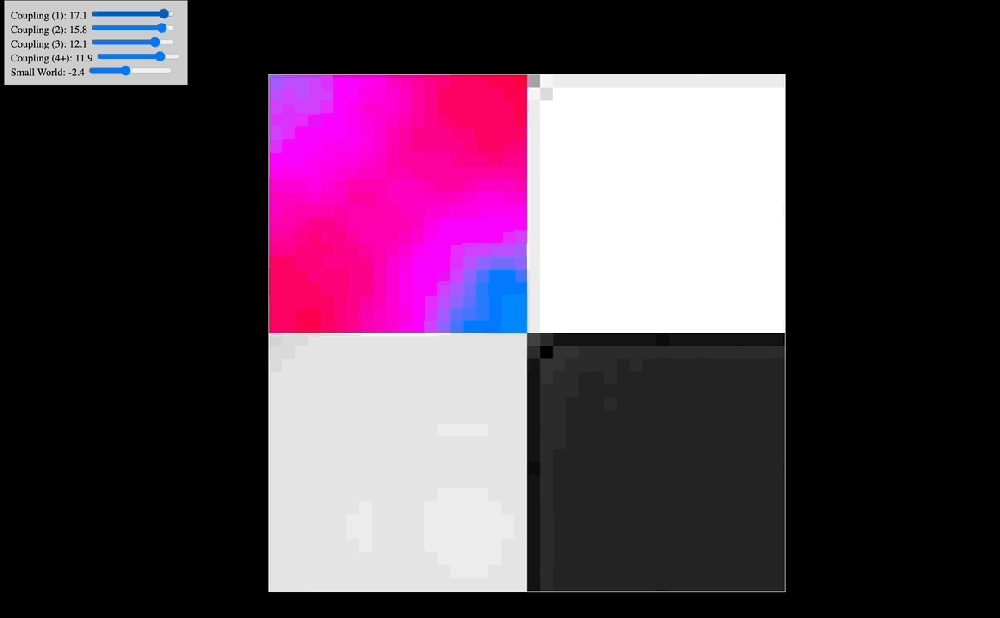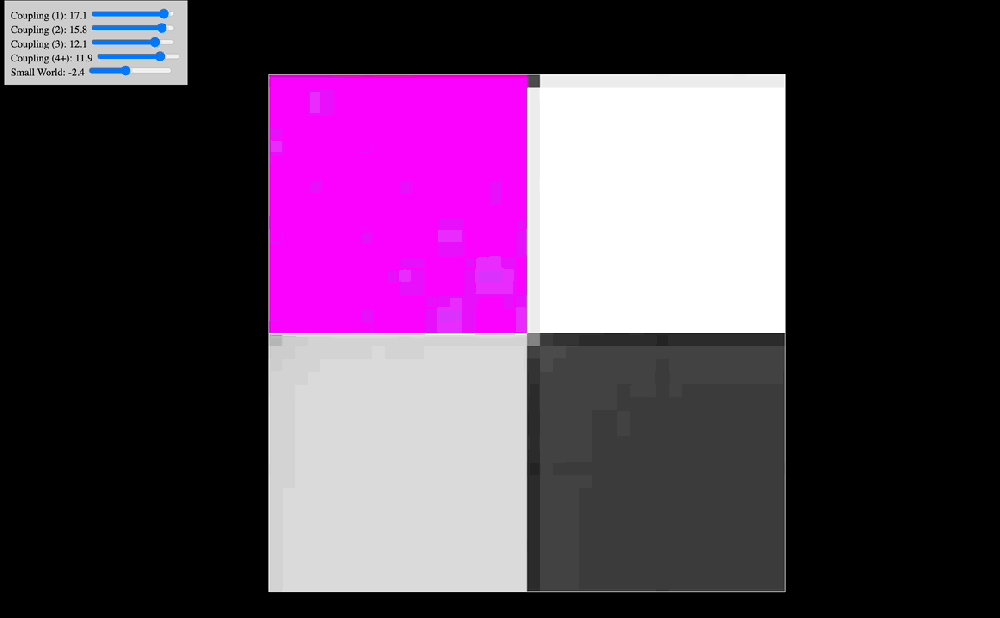
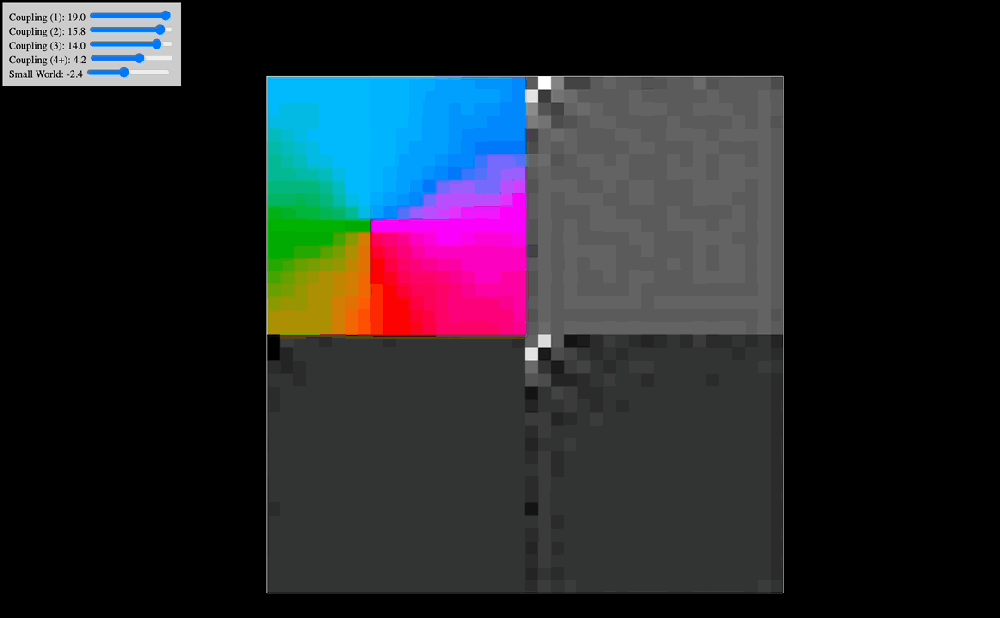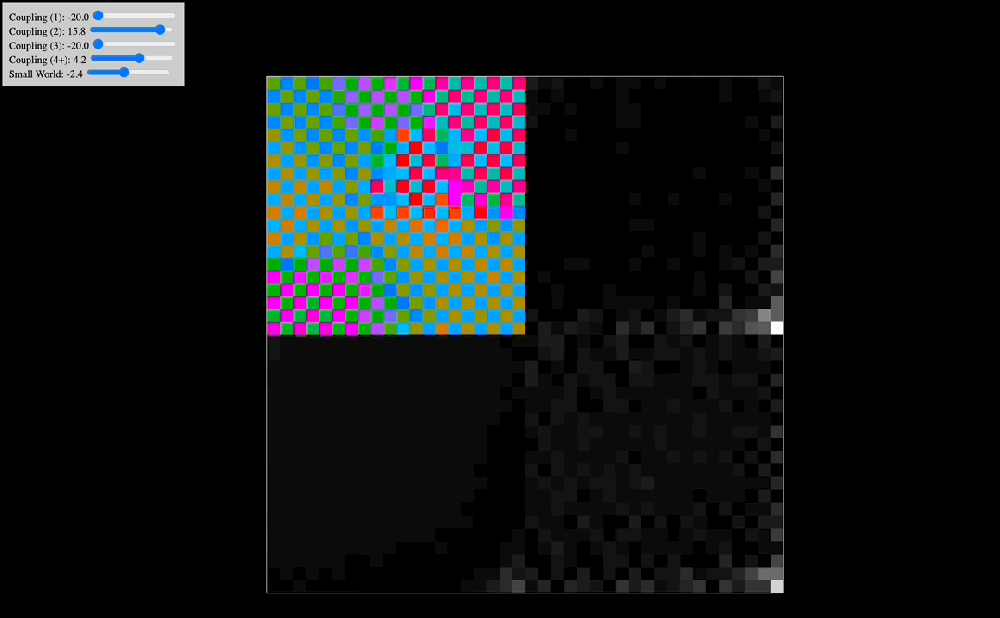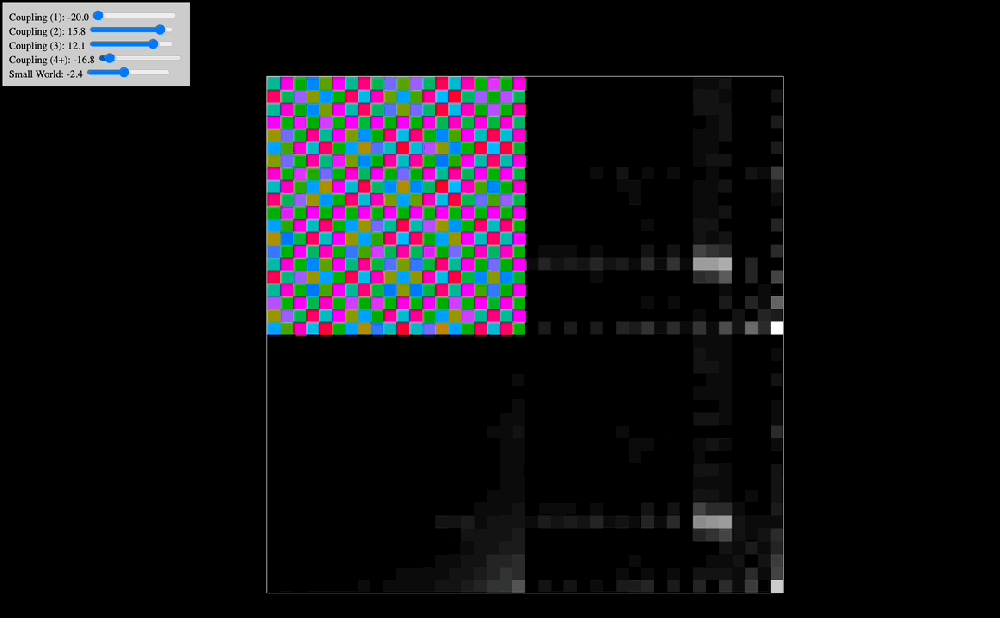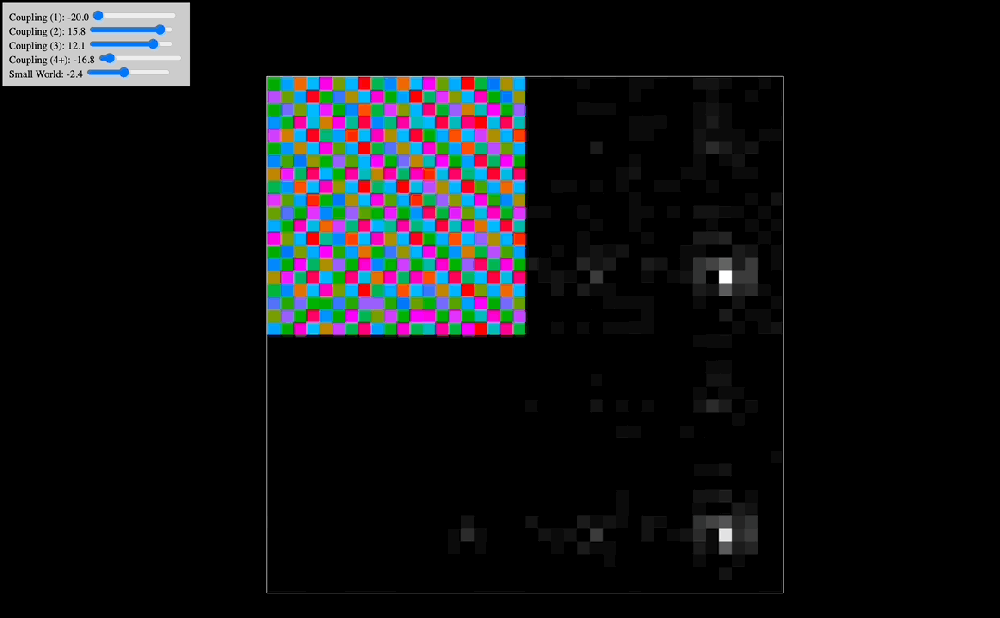

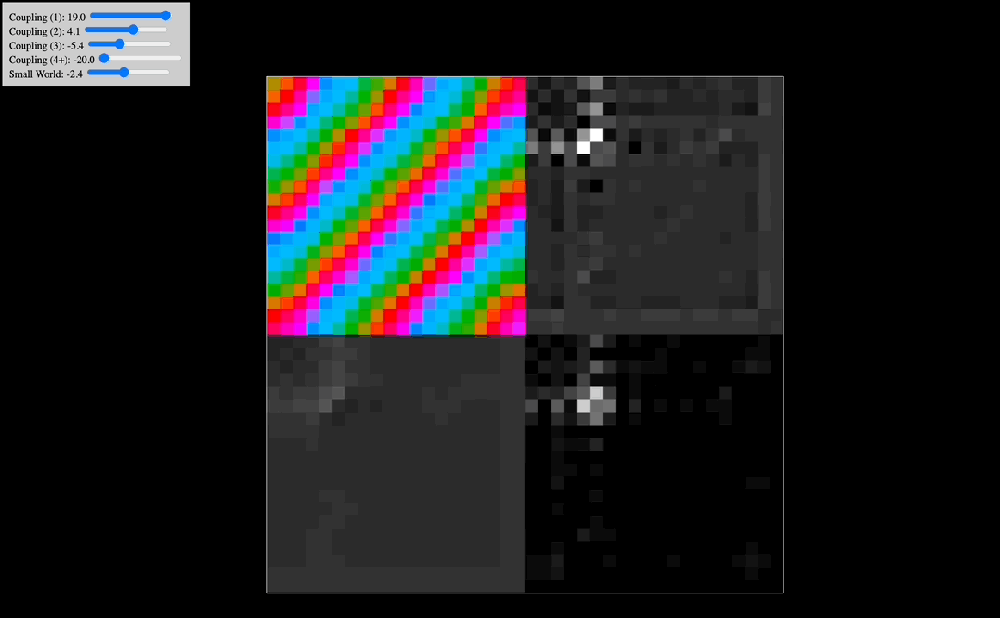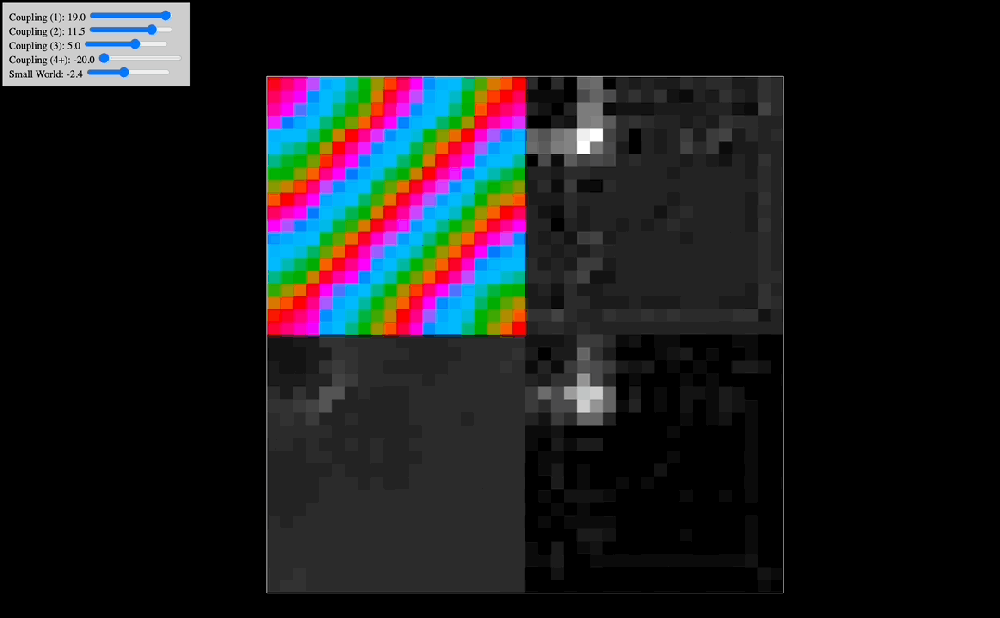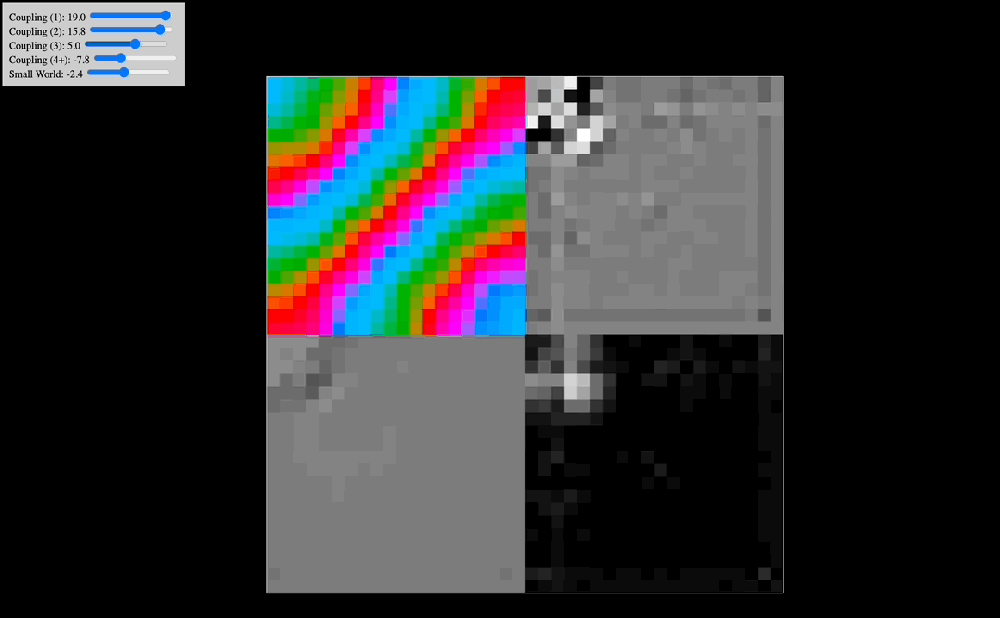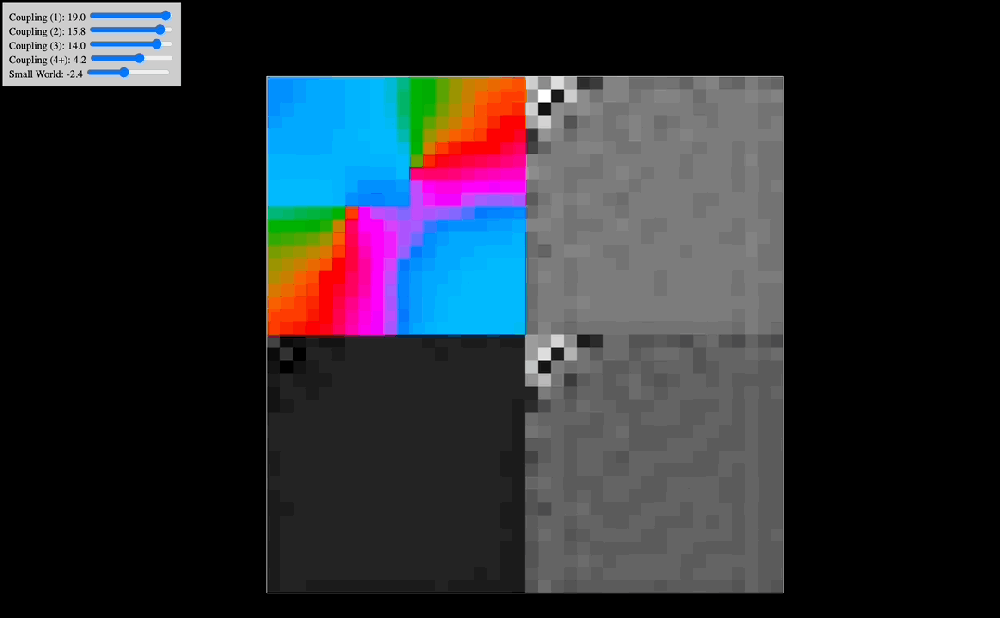
The animations above show: coupling kernel for a 2D system of coupled oscillators, shown on the top-left quadrant. Top-right quadrant is the Discrete Cosine Transform of the 2D plate of oscillators. Bottom-left is a temporal low-pass filter on the DCT. Bottom-right is a temporal high-pass filter on the DCT. Source: Internal QRI tool (public release forthcoming)
In November of last year at a QRI work retreat we stumbled upon two key frameworks that directly address these concepts in the research of Marco Aqil. Namely, CHAOSS (Connectome-Harmonic Analysis Of Spatiotemporal Spectra) and Divisive Normalization. In those works we find how the coupling kernel serves as the critical bridge between local neural activity and global brain-wide behavior. This connection emerges from deep mathematical principles explored in the CHAOSS framework. As we scale up from individual neural circuits to larger networks, the distribution of power across different harmonics of the system becomes accessible through modulation of the coupling kernel. CHAOSS reveals how the eigenmodes (in this case corresponding to “connectome harmonics”) of our structural wiring give rise to global patterns of brain activity. When provided appropriate coupling parameters, neural systems resonate with specific structural frequencies, producing macroscopic standing waves that unify and reorganize local activation patterns.
The link between molecular mechanisms and coupling kernels becomes particularly clear through divisive normalization. This canonical neural computation principle describes how a neuron’s response to input is modulated by the activity of surrounding neurons through specific molecular pathways. Different receptor systems (like 5-HT2A and 5-HT1A) can alter these normalization circuits in characteristic ways (perhaps ultimately explaining the implementation-level effects discussed in Serotonin and brain function: a tale of two receptors (2017, Carhart-Harris, Nutt)). When we map this to our coupling kernel framework, we see that changes in divisive normalization directly translate to changes in the coupling kernel’s shape. For instance, 5-HT2A activation might enhance local inhibition while simultaneously strengthening medium-range excitation, creating the alternating positive-negative coupling pattern characteristic of DMT states. Conversely, 5-HT1A activation might promote more uniform positive coupling across distances, explaining 5-MeO-DMT’s tendency toward global coherence. This provides a concrete mechanistic bridge from receptor activation to field topology: receptor binding → altered divisive normalization → modified coupling kernel → changed field topology. It’s a beautiful example of how a relatively simple molecular change can propagate through multiple scales to create profound alterations in consciousness.
In the CHAOSS framework, each brain region and pathway is represented as a node and edge on a distance-weighted graph. The framework applies spatiotemporal graph filters that act as coupling kernels, encoding how each node influences and is influenced by its neighbors across multiple time scales. By systematically adjusting parameters for excitatory and inhibitory interactions, we can effectively “scan” the connectome’s harmonic space: certain configurations produce stable resonance, others generate traveling waves or chaotic patterns, and some configurations may induce boundary-dissolving states that might prevent the formation of gestalts, and so on. The point being that it can be rigorously shown that in a system of coupled oscillators, a spatial (or temporal) coupling kernel can effectively “tune into” global resonant modes of the entire system.
At the very lowest-level, Marco’s work on Divisive Normalization suggests that there is a mode of canonical neural computation, where the response from a population of neurons to a given input signal is mediated by the surrounding context, a circuit that involves neurons that respond to different neurotransmitter systems. In particular, here we have a bridge that links the very low-level neural circuits to the coupling kernels, which in turn excites specific harmonic resonant modes of the entire system. In other words, the coupling kernel is a sort of intermediate “meso-level” structure that provides system-wide dynamic control of resonance and can be derived as a function of the balance between different neuronal populations that respond to specific neurotransmitters (learn more).
The result of encountering this research is that we now have a crisp conceptual explanation for how coupling kernels might arise (and be controlled by) low-level circuitry, and also why (in a mathematically rigorous way) such kernels can tune into global resonant modes. It therefore starts to look like there is a potentially highly rigorous link between the insights that come from QRI’s Think Tank “taking phenomenology seriously” approach and the current leading academic theories of how drugs affect perception.
2. Geometric Constraints on Coupling Effects
With the above said, the human organism is really complex, and so it is natural to ask: where exactly does the coupling kernel apply to? As argued recently we propose that it would be highly parsimonious if the coupling kernel applied to a range of systems at the same time: the visual cortex, the auditory cortex, the somatosensory cortex, the peripheral nervous system, and even the vasculature. Here the conceptual framework would say that a given drug might change the way low-level circuitry results in divisive normalization with specific constants, and that this change is applied to a wide range of systems. When you take LSD you get a characteristic “vibrational pattern” that might be present in, say, both the vascular system and the visual cortex at the same time. The underlying change is very simple, but the resulting effect is system-dependent due to the characteristic geometry and topology of each subsystem that is affected.
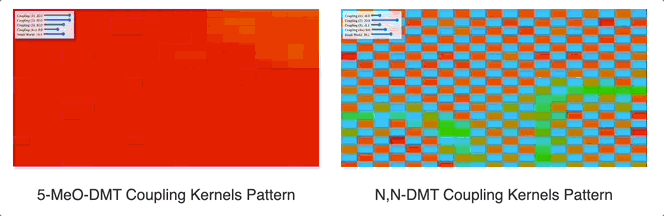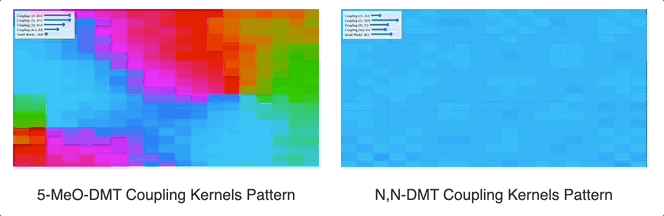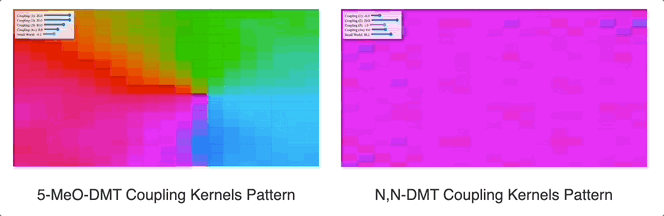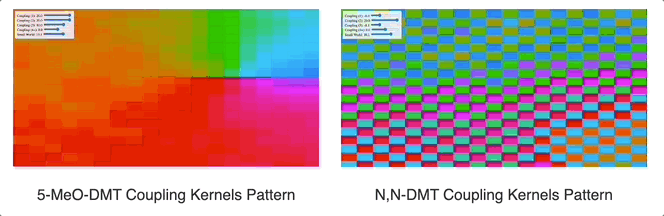
I think that a key insight we ought to work with is that the geometry of the system on which a coupling kernel operates fundamentally determines its high-level effects. A particularly striking example of how geometry shapes coupling kernel effects can be seen in the contrast between the visual cortex and the vasculature system. The visual cortex, organized as a hierarchical geometric network with distinct layers and columnar organization, responds to coupling kernels in ways that reflect its structural hierarchy. When a DMT-like kernel (alternating positive-negative coupling constants) is applied, it generates competing clusters of coherence at different scales of the hierarchy. This manifests phenomenologically as the characteristic layered, fractal-like visual patterns reported in DMT experiences, where similar motifs appear nested at multiple scales. In contrast, a 5-MeO-DMT-like kernel (uniformly positive coupling) drives the hierarchical network toward global synchronization, potentially contributing to the reported dissolution of visual structure in 5-MeO-DMT experiences.
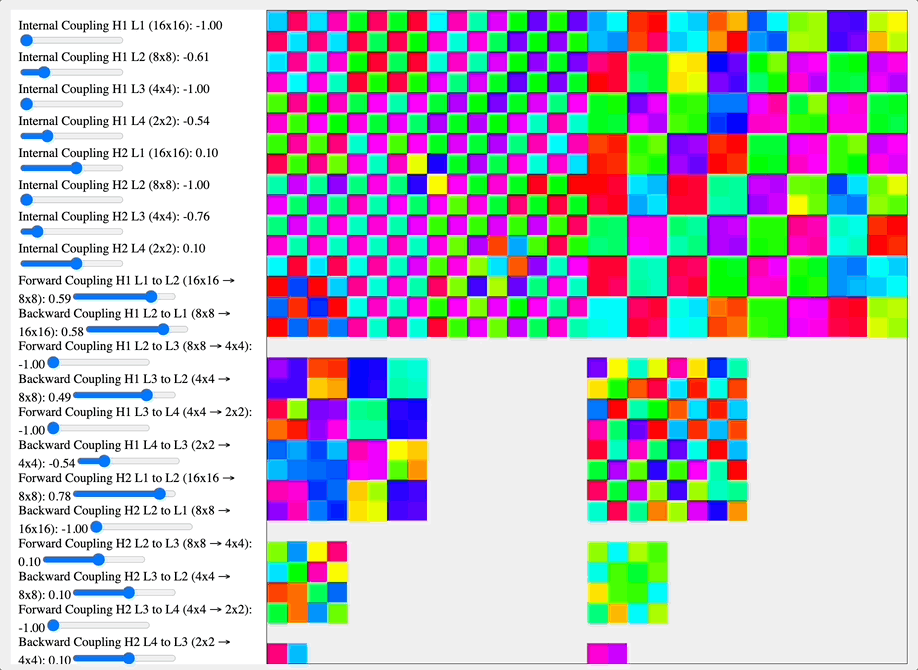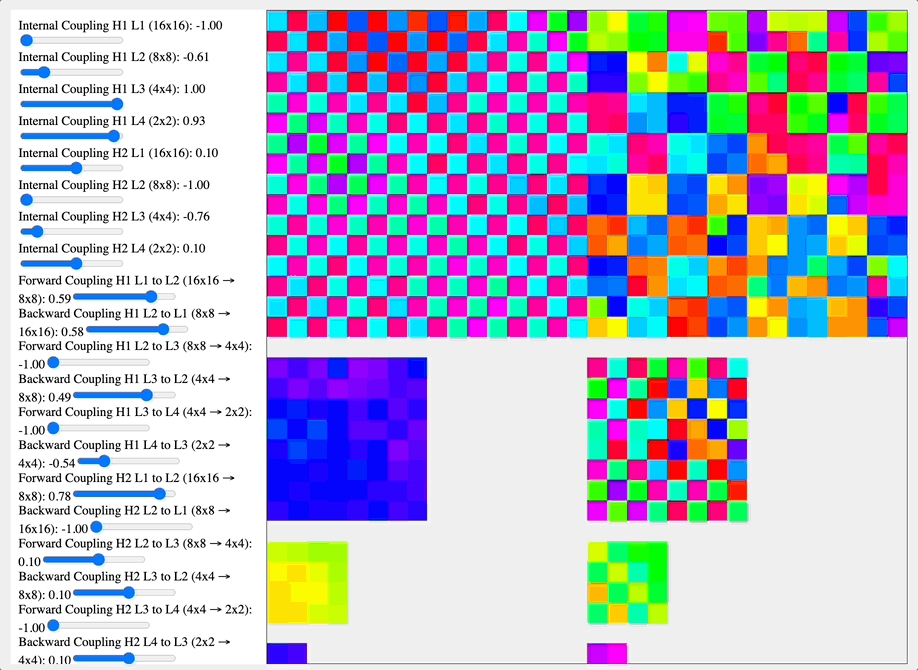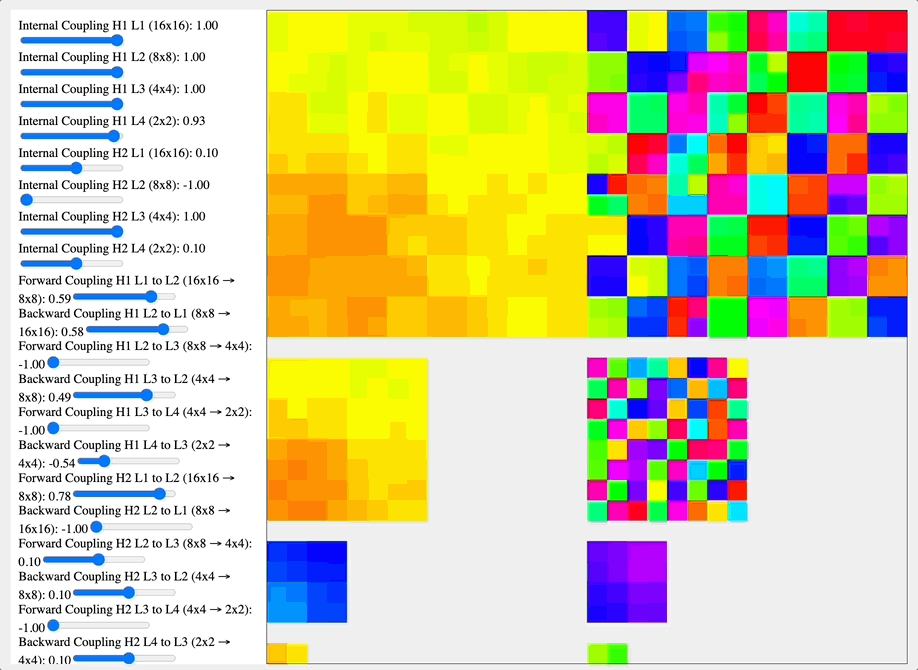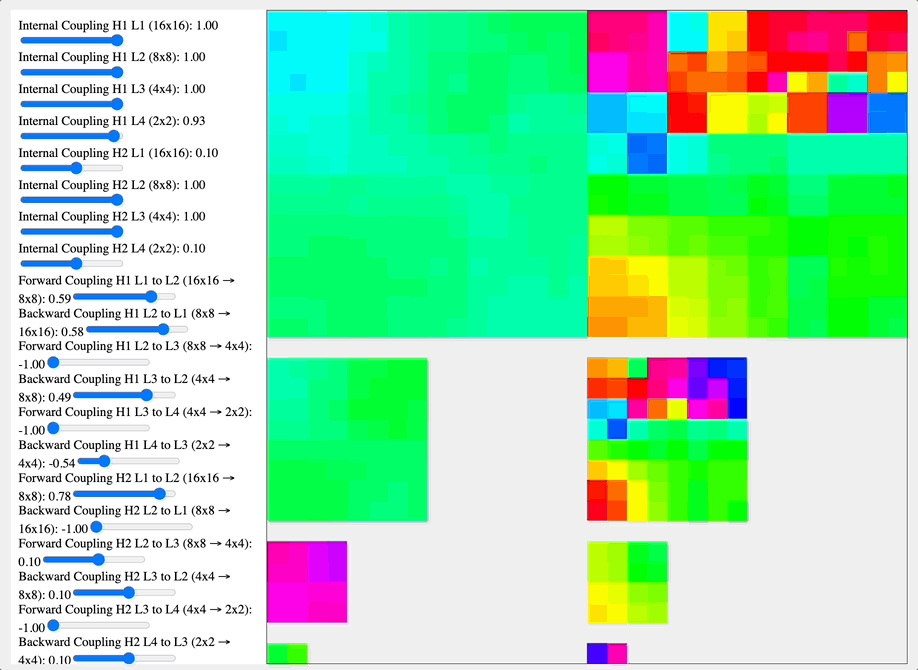
Simulation comparing coupling kernels across a hierarchical network of feature-selective layers (16×16 to 2×2), showing how different coupling coefficients between and within layers affect pattern formation. The DMT-like kernel (-1.0 near-neighbor coupling) generates competing checkerboard patterns at multiple spatial frequencies, while the 5-MeO-DMT-like kernel (positive coupling coefficients) drives convergence toward larger coherent patches. These distinct coupling dynamics mirror how these compounds might modulate hierarchical neural architectures like the visual cortex.
Source: Internal QRI tool (public release forthcoming)
The vasculature system, on the other hand, exemplifies a scale-free network with its branching architecture. Here, the same coupling kernels produce markedly different effects. In the vasculature, a DMT-like kernel would tend to create competing clusters of coherence primarily at bifurcation points, where vessels branch. This could explain some of the characteristic bodily sensations reported during DMT experiences, such as the feeling of energy concentrating at specific points in the body. When a 5-MeO-DMT-like kernel is applied to this scale-free network, it drives the entire system toward global phase synchronization, potentially contributing to the reports of profound bodily dissolution and unity experiences (cf. when you experience a dysphoric 5-MeO-DMT response oftentimes this can be traced to a mostly coherent but slightly off pattern of flow, where “energy” strongly aggregates in a specific point, cf. Arataki’s Guide to 5-MeO-DMT).
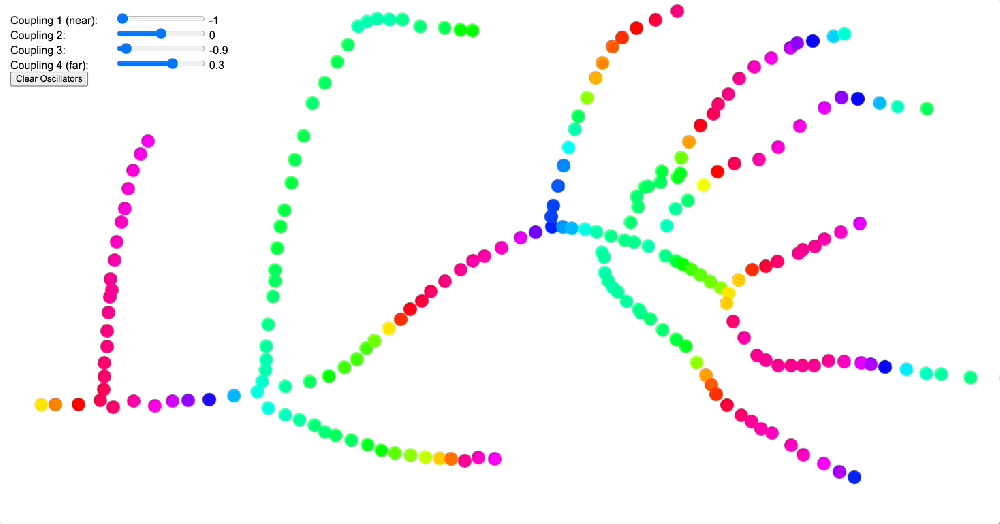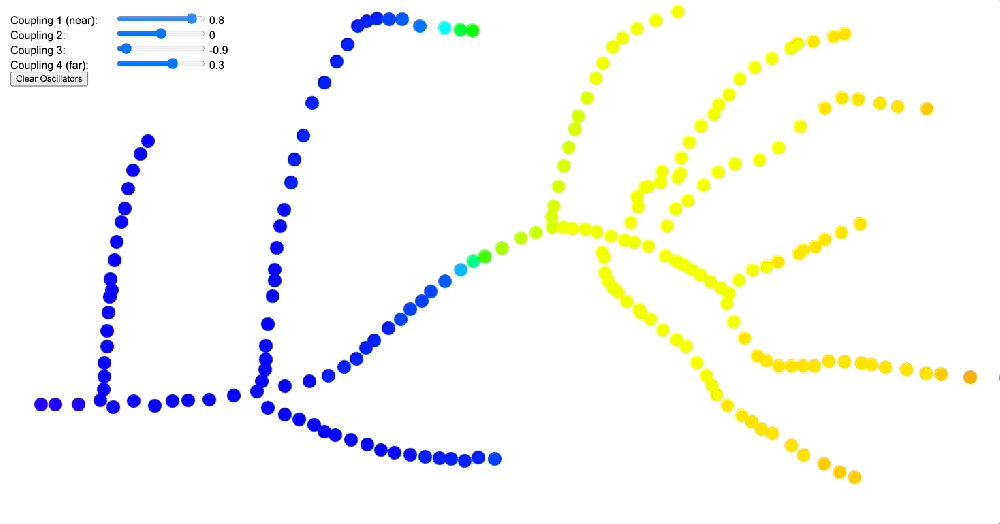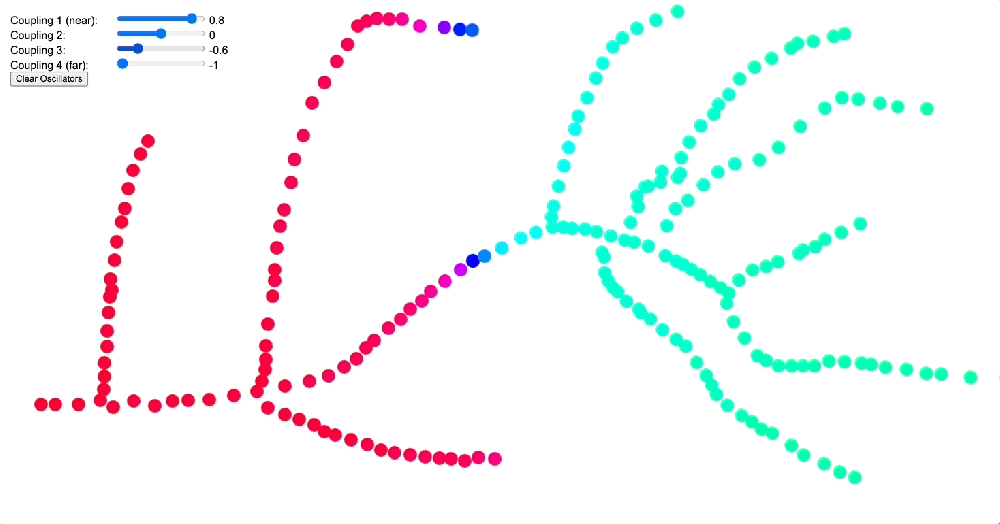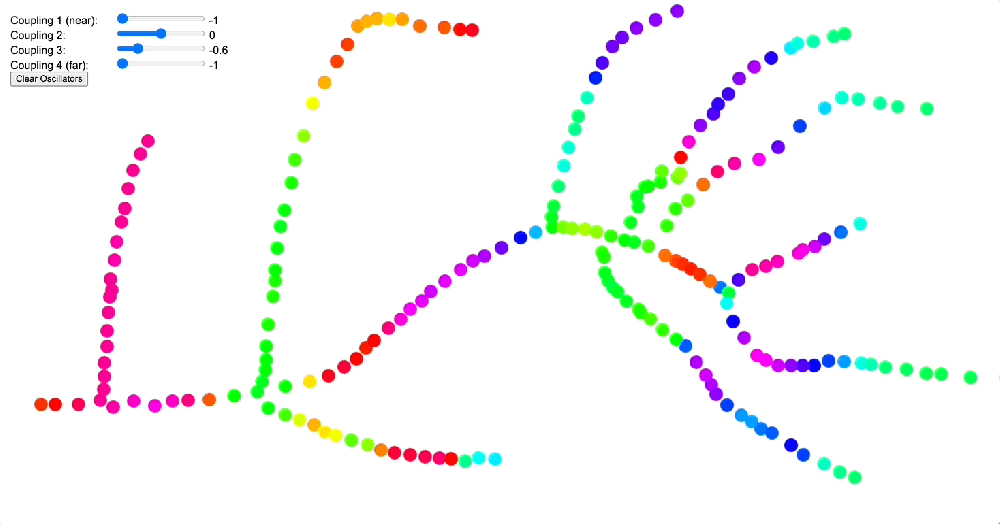
Simulation comparing different coupling kernels (DMT-like vs 5-MeO-DMT-like) applied to a 1.5D fractal branching network, showing how modified coupling parameters affect phase coherence and signal propagation. The DMT-like kernel produces competing clusters of coherence at bifurcation points, while the 5-MeO-DMT kernel drives the system toward global phase synchronization – patterns that could explain how these compounds differently affect branching biological systems like the vasculature or peripheral nervous system.
Source: Internal QRI tool (public release forthcoming)
This framework helps explain how a single pharmacological intervention, by modifying coupling kernels through changes in divisive normalization, can produce such diverse phenomenological effects across different biological systems. The geometry of each system acts as a filter, transforming the same basic change in coupling parameters into system-specific resonant patterns. This provides a unified explanation for how psychedelics can simultaneously affect visual perception, bodily sensation, and cognitive processes, while maintaining characteristic differences between compounds based on their specific coupling kernel signatures.
The notion of a continuous graph-based system dissolves traditional distinctions between regional oscillator networks and global wave phenomena into a single multifaceted gem of coupled states. By shaping coupling kernels, we effectively tune into specific connectome harmonics, instantiating global resonant modes that underlie everything from coherent sensory integration to altered states of consciousness.
3. Network Geometry Interactions and Projective Intelligence
A fundamental computational principle emerges from the interaction between networks of different geometries and topologies. This principle underlies what we might call “projective intelligence” or more broadly, mapping/functional intelligence. The interaction between the 2D visual field and 3D somatic field provides a prime example of this principle in action.
Consider how we understand a complex three-dimensional object like a teapot. Our visual system receives a 2D projection, but we comprehend the object’s full 3D structure through an intricate dance between visual and somatic representations. As we observe the teapot from different angles, our visual system detects various symmetries and patterns in the 2D projections: perhaps the circular rim of the spout, the elliptical body, the handle’s curve. These 2D patterns, processed through the visual cortex’s hierarchical geometric network, generate characteristic resonant modes. Simultaneously, our somatic system maintains a 3D spatial representation where we can “map” these detected symmetries. The brain effectively “paints” the symmetries found in the 2D visual field onto the 3D somatic representation, creating a rich multi-modal representation of the object.

This process involves multiple parallel mappings between sensory fields, each governed by its own coupling kernel. The visual field might have one kernel that helps identify continuous contours, while another kernel in the somatic field maintains spatial relationships. These kernels can synchronize or “meet in resonance” when the mappings between fields align correctly, giving rise to stable multimodal representations. When we grasp the teapot, for instance, the tactile feedback generates somatic resonant modes that match our visually-derived expectations, reinforcing our understanding of the object’s structure (many thanks to Wystan, Roger, Cube Flipper, and Arataki for many discussions on this topic and their original contributions thereof – the fact that visual sensations devoid of somatic coupling have a very different quality in particular was a brilliant observation by Roger that fomented a lot of insights in our sphere).
The necessity of interfacing between spaces of different dimensionality (e.g. 3D somatic space and 2.5D visual space) creates interesting constraints. In systems exhibiting resonant modes emergent from coupled oscillator wiring, energy minimization occurs precisely where waves achieve low-energy configurations in both interfacing spaces simultaneously. This requires finding both an optimal projection between spaces and appropriate coupling kernels that allow the resulting space to behave as if it were unified.
Remarkably, this framework suggests that our cognitive ability to understand complex objects and spaces emerges from the brain’s capacity to maintain multiple concurrent mappings between sensory fields of different dimensionalities. Each mapping can be thought of as a kind of “cross-modal resonance bridge,” where coupling kernels in different sensory domains synchronize to create stable, coherent representations. When this level of coherence is achieved, the waves cannot detect the underlying projective dynamic: there simply is no “internal distinction” to be found in an otherwise complex system that typically maintains many differences between the spaces it maps. At the limit, the perfect alignment between the various mappings and coupling kernels of all sensory fields is what we hypothesize explains meditative cessations.
This multiple-mapping approach might explain phenomena like the McGurk effect, where visual and auditory information integrate to create a unified perception, or the rubber hand illusion, where visual and tactile fields can be realigned to incorporate external objects into our body schema. In each case, coupling kernels in different sensory domains synchronize to create new stable configurations that bridge dimensional and modal gaps.
The framework also provides insight into how psychedelics might affect these cross-modal mappings. DMT, for instance, might introduce competing clusters of coherence across different sensory domains, leading to novel and sometimes conflicting cross-modal associations. In contrast, 5-MeO-DMT might drive all mappings toward global synchronization, along which characteristic system-wide synchronization effects manifest, potentially explaining the reported dissolution of distinctions between sensory modalities and the experience of unified consciousness.
Understanding consciousness as a system of interacting dimensionally-distinct fields, each with their own coupling kernels that can synchronize and resonate with each other, offers a powerful new way to think about both ordinary perception and altered states. It suggests that our rich experiential world emerges from the brain’s ability to maintain and synchronize multiple parallel mappings between sensory domains of different dimensionalities, creating a unified experience from fundamentally distinct representational spaces.
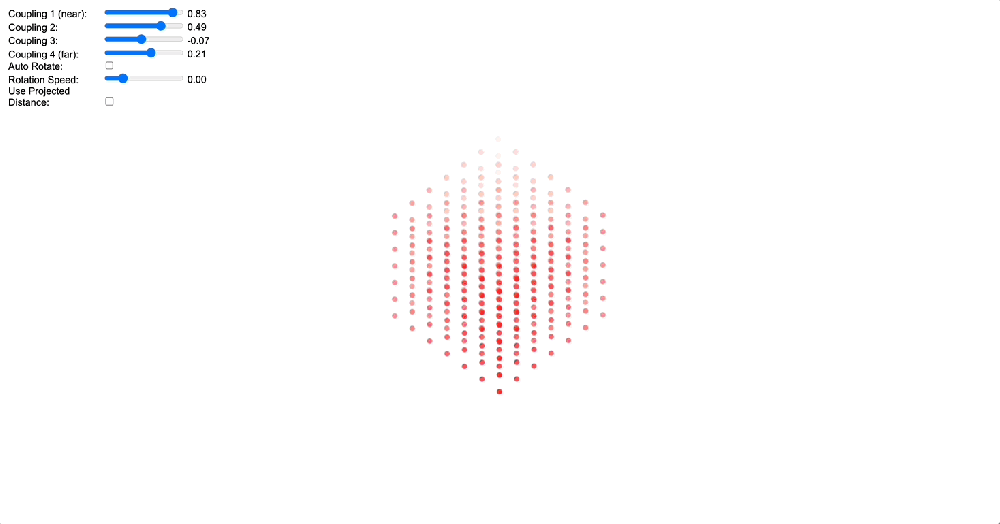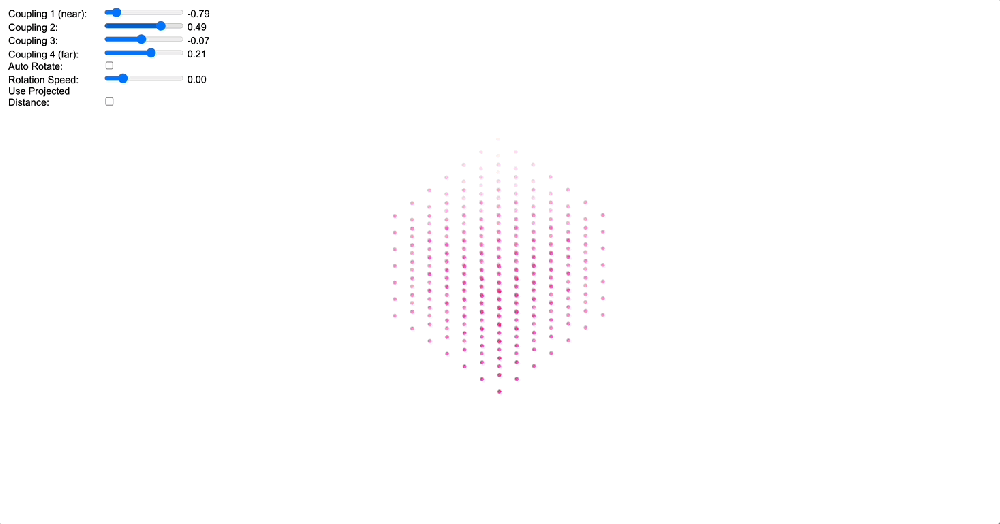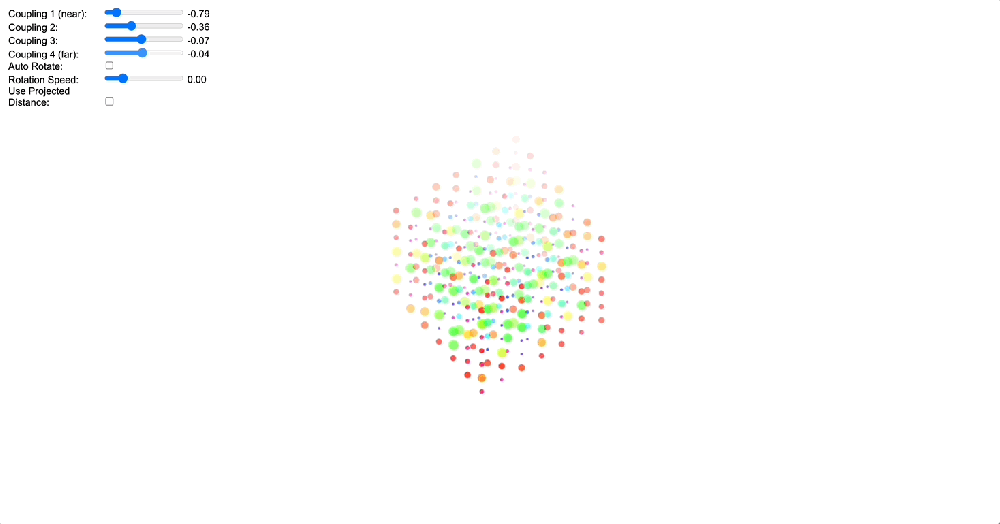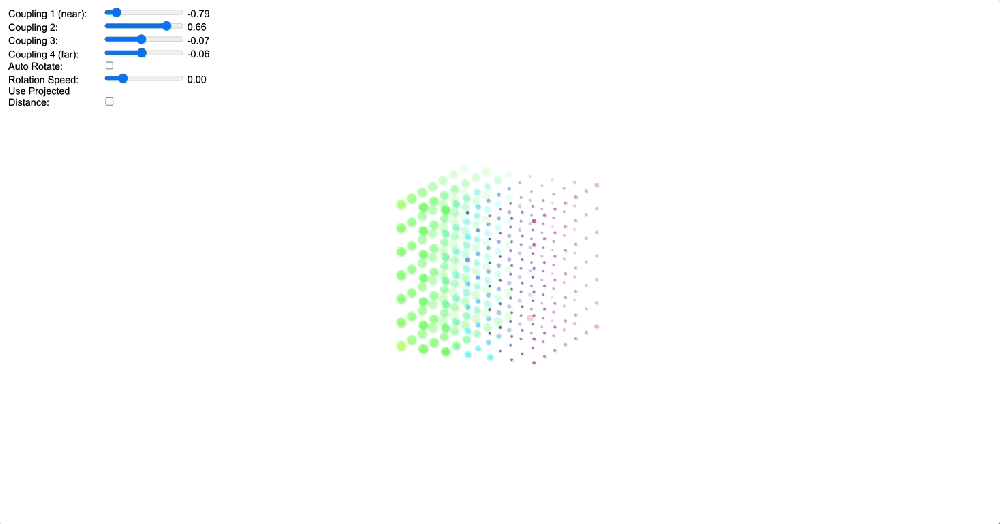
4. Topological Solution to the Boundary Problem
Here’s where the framework really starts to come together: if we identify fields of physics with fields of qualia (a field-based version of panpsychism), then the boundaries between subjects could be topological in nature. Specifically, where magnetic field lines “loop around” to form closed pockets, we might find individual moments of experience. These pockets aren’t arbitrary or observer-dependent: they’re ontologically real features of the electromagnetic field that naturally segment conscious experience (note: I will leave aside for the time being the discussion about the ontological reality of the EM field, but suffice to say that even if the EM field is an abstraction atop the more fundamental ontology of reality, we believe topological segmentation could then apply to that deeper reality).
This provides a compelling solution to the boundary problem: what stops phenomenal binding from expanding indefinitely? The answer lies in the topology of the field itself. When field lines close into loops, they create genuine physical boundaries that can persist and evolve as unified wholes. These boundaries are frame-invariant (preserving properties under coordinate transformations), support weak emergence without requiring strong emergence, and explain how conscious systems can exert downward causation on their constituent parts through resonance effects.
5. Electromagnetic Field Topology and its Modulation
To demonstrate how coupling kernels create and control these field boundaries, we’ve developed three key simulations showing electric oscillators embedded in magnetic fields. By visualizing the resulting field configurations across different geometries – 2D grids, circular arrangements, and branching structures – we can directly observe how coupling kernels shape field topology.
When we apply a DMT-like kernel (alternating positive-negative coupling constants at different distances), we see an explosion of topological complexity in which multiple vortices and anti-vortices emerge, creating a diverse patterns of nested field structures. The same kernel creates characteristic patterns in each geometry, but always tends toward complexification. In contrast, applying a 5-MeO-DMT-like kernel (uniformly positive coupling) causes these complex structures to simplify dramatically, often collapsing into a single large vortex or even completely smooth field lines.
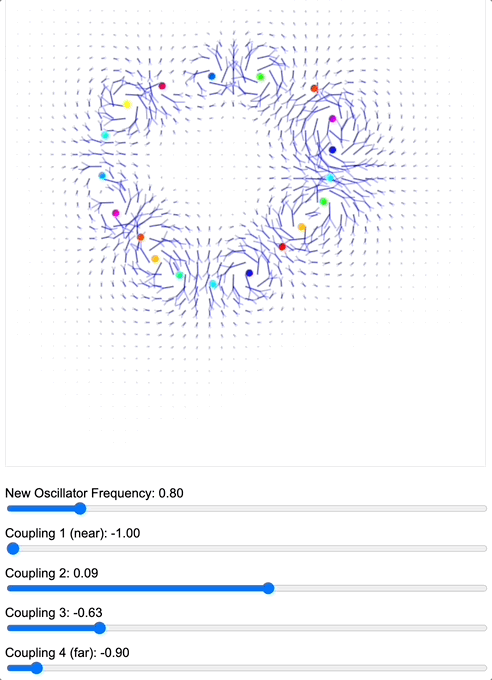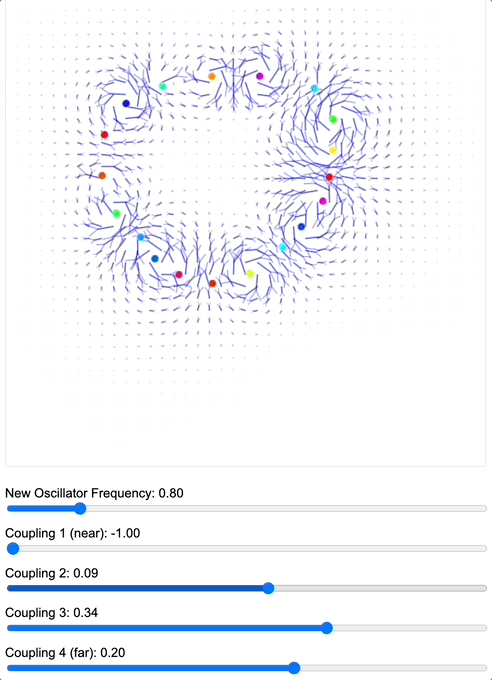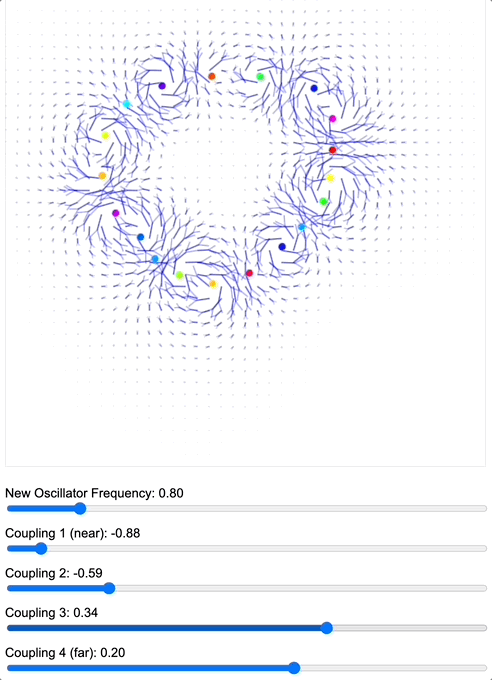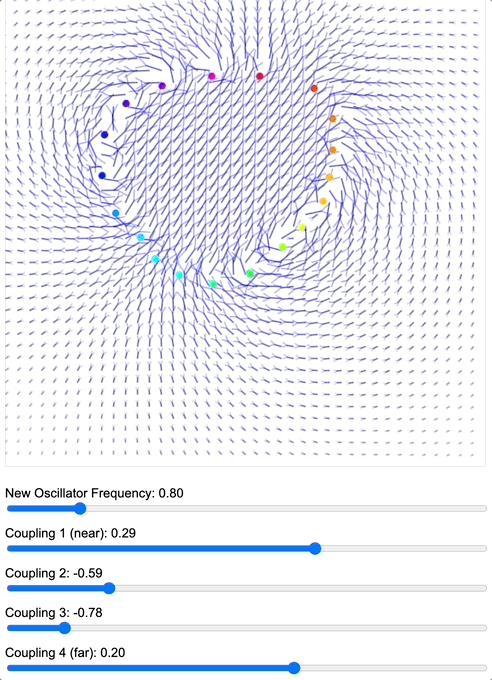
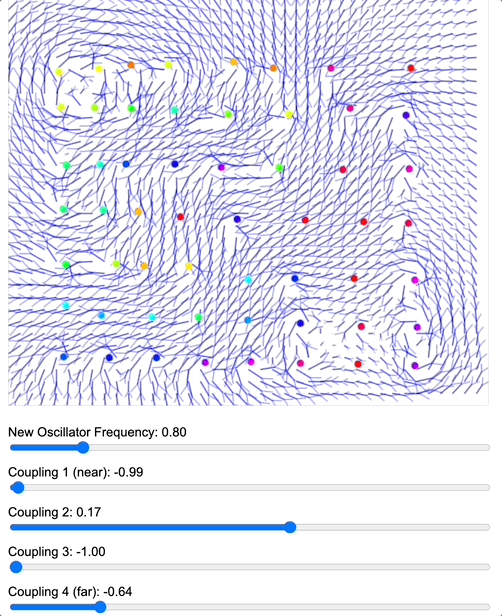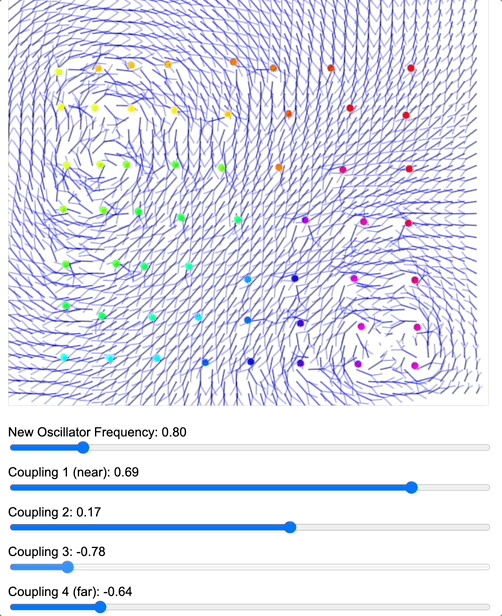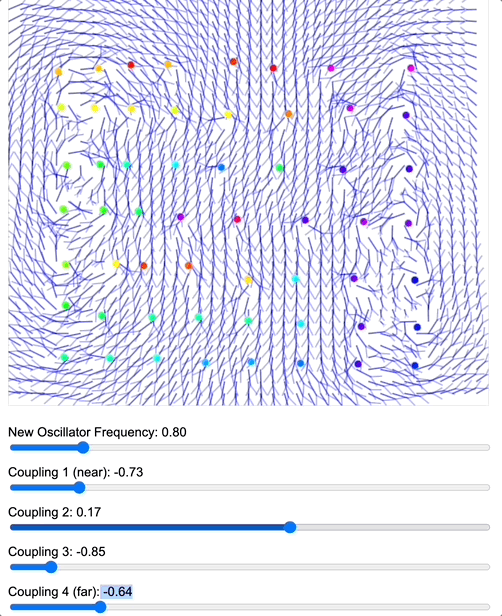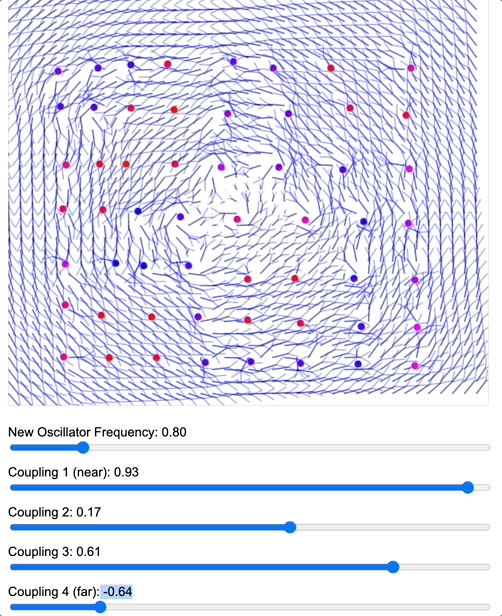
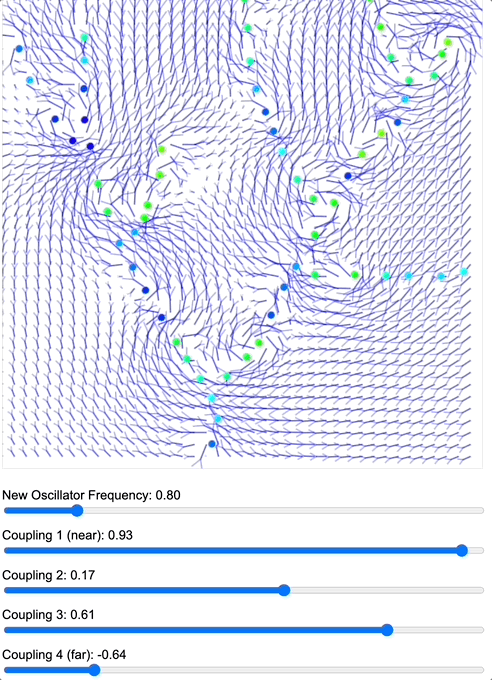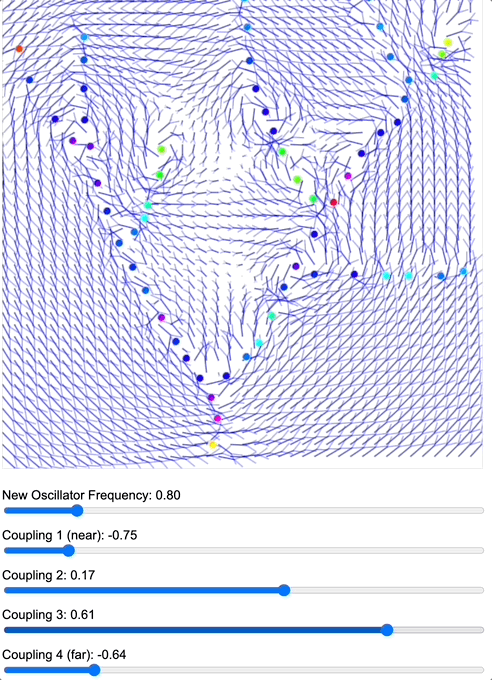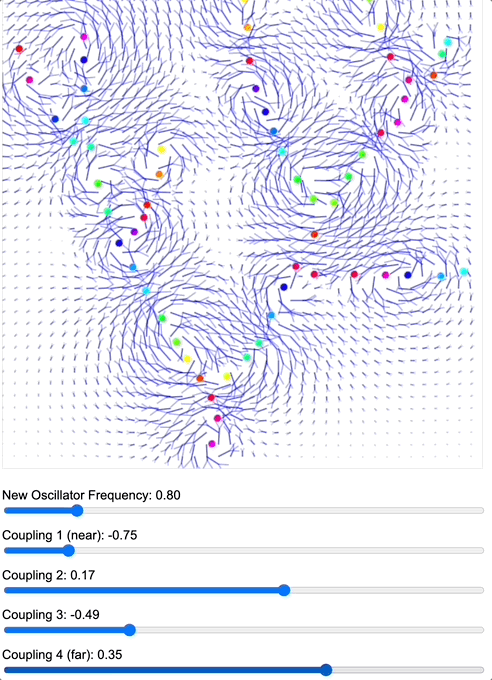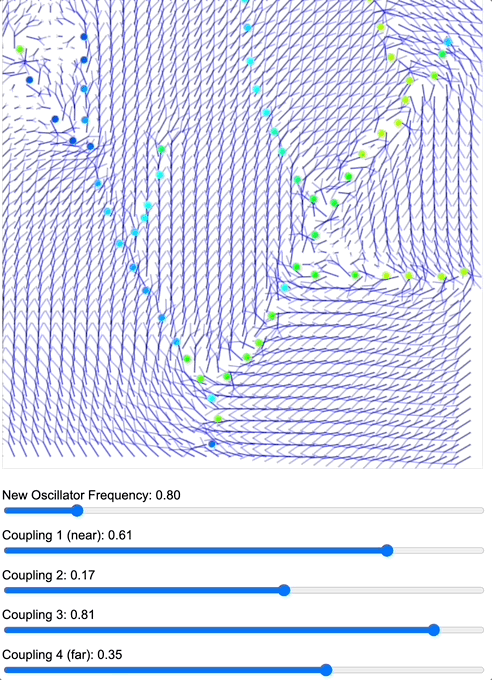
Coupled oscillators in a 2D space whose phase is interpreted as electric oscillations are embeded in a magnetic field whose topology becomes mediated by the coupling kernel. Source: Internal QRI tool (public release forthcoming)
[Note: These are still 2D simulations – a full 3D electromagnetic simulation is in development and will likely reveal even richer topological dynamics. However, even these simplified models provide striking evidence for how coupling kernels can control field topology.]
6. 5-MeO-DMT and Topological Simplification
The remarkable alignment between our theoretical predictions and actual psychedelic experiences becomes clear when we examine 5-MeO-DMT states. As documented in Cube Flipper’s “5-MeO-DMT: A Crash Course in Phenomenal Field Topology” (2024), these experiences frequently involve the systematic disentangling or annihilation of local field perturbations (“topological defects”) over time. Subjects report a progressive dissolution of boundaries and eventual sense of absolute unity or “oneness.” Significantly, recent EEG analysis of 5-MeO-DMT experiences also reveal remarkable topological properties, which we’re currently trying to derive from a 3D model of the brain in light of altered coupled kernels.


Source: Cube Flipper’s HEART essay on 5-MeO-DMT and field topology.
This phenomenology maps really well onto what our electromagnetic simulations predict: a 5-MeO-DMT-like coupling kernel transforms networks of swirling singularities into simplified field configurations. The effect isn’t limited to any particular neural subsystem: it appears to drive global topological simplification across multiple scales and geometries, explaining both the intensity and the consistency of the experience across subjects. In turn, a lot of the characteristic phenomenological features of 5-MeO-DMT might find their core generator as the interaction between a very positive coupling kernel and the interesting relationships between different sensory fields as they try to map onto each other to minimize dissonance. At the peak of a breakthrough experience, typically this culminates in what appears as a global multimodal coherent state, where presumably all the sensory fields have found a mapping to each other such that the waves in each look exactly the same: the recipe for a zero informational state of consciousness. A whiteout.
What’s particularly fascinating is that this framework suggests normal waking consciousness might represent a sweet spot of topological complexity. It carries enough structure to maintain a stable sense of self and world, but not so little as to dissolve completely (as in 5-MeO-DMT states). Each topological defect could be thought of as a kind of “perspectival anchor” in the field. As these defects systematically dissolve under 5-MeO-DMT, we would expect exactly what subjects report: a progressive loss of distinct perspectives culminating in a state of pure unity. Perhaps sleep and dreaming could be also interpreted through this lens: during periods of wakefulness we slowly but surely accumulate topological defects; sleep and dreaming might be a process of topological simplification where the topological defects aggregate and cancel out. Notice next time you find yourself in a hypnagogic state how it feels like to “let go of the central grasping to experience” and the subsequent fast “unraveling” of the field of experience. Much more to say about this in the future (a topological simplification theory of sleep).
7. Coupling Kernels and Field Topology
The mechanism by which coupling kernels control field topology reveals something really deep, abstract, and yet applied about consciousness: the same mathematical object (the coupling kernel) can simultaneously modulate both neural dynamics and electromagnetic field structure. This isn’t just correlation: we are talking about a direct causal chain from molecular interaction to conscious experience and back. Precisely the sort of structure we want in order to both ground the topological boundary problem solution in neurophysiology and avoid epiphenomenalism (since the field topology feeds back into neural activity, cf. local field potentials).
Consider how this works: when we apply a coupling kernel to a network of electric oscillators, we’re not just changing their relative phases. We’re also sculpting the magnetic field they generate. Each oscillator contributes to the local magnetic field, and the coupling kernel determines how these contributions interfere. Positive coupling between nearby oscillators tends to align their fields, creating smooth, continuous field lines. Negative coupling creates discontinuities and vortices. The resulting field topology emerges from these collective interactions, yet acts back on the system as a unified whole through electromagnetic induction.
What’s particularly elegant about this mechanism is its scale-invariance. Whether we’re looking at ion channels in a single neuron or large-scale brain networks, the same principles apply. The coupling kernel acts as a kind of “field-shaping operator” that can be applied at any scale where electromagnetic interactions matter. This helps explain why psychedelics, which presumably modify coupling kernels through receptor activation, can have such profound and coherent effects across multiple levels of brain organization.
8. DMT vs 5-MeO-DMT Effects
With this mechanism in hand, we can now understand the radically different effects of DMT and 5-MeO-DMT in a new light. The key insight is that these compounds don’t just change what we experience. They transform the very structure of the field that gives rise to bound experiences.
DMT appears to implement a coupling kernel with a characteristic Mexican-hat profile: strong negative coupling at short distances combined with positive coupling at medium distances. When applied to neural networks, this creates competing clusters of coherence. But more fundamentally, it generates a field topology rich in stable vortices and anti-vortices. Each of these topological features acts as a semi-independent center of field organization – a kind of local “observer” within the larger field.
This helps explain one of the most striking aspects of DMT experiences: the encounter with apparently autonomous entities or beings. If each major topological defect in the field functions as a distinct locus of observation, then the DMT state literally creates multiple valid perspectives within the same field of consciousness. The geometric patterns commonly reported might reflect the larger-scale organization of these topological features – the way they naturally arrange themselves in space according to electromagnetic field dynamics.
The bizarre yet consistent nature of DMT entity encounters takes on new meaning in this framework. These entities often seem to exist in spaces with impossible geometries, yet interact with each other and the observer in systematic ways. This is exactly what we’d expect if they represent stable topological features in a complexified electromagnetic field: they would follow precise mathematical rules while potentially violating our usual intuitions about space and perspective. Even our notion of a central observer and object of observation; the DMT space has many overlapping “points of view” derived from the complex topology of the field.
These insights stand in stark contrast to 5-MeO-DMT’s effects, but they emerge from the same underlying mechanism. They also suggest new research directions. For instance, we might be able to predict specific patterns of field organization under different compounds by analyzing their receptor binding profiles in terms of their implied coupling kernels. This could eventually allow us to engineer specific consciousness-altering effects by designing molecules (or drug cocktails) that implement particular coupling kernel shapes.
9. Paths and Experience: The Path Integral of Perspectives
Here’s where we get to be both mathematically precise and delightfully speculative: I propose that the mapping between field topology and phenomenology is best understood through the path integral of all possible perspectives within a topological pocket. This isn’t just mathematical fancy – it’s a necessary move once we realize that consciousness doesn’t always have a center.
Think about it: we’re used to consciousness having a kind of “screen” quality, where everything is presented to a singular point of view. But this is just one possible configuration(!). On DMT, for instance, experiencers often report accessing topological extrema instantaneously, as if consciousness could compress or tunnel through its own geometry to find patterns and symmetries. This suggests our usual centered experience might be more of a special case – perhaps we’re too attached (literally, in terms of field topology) to a central vortex that geometrizes experience in a familiar way.
When we consider the full range of possible field topologies, things get wonderfully weird (but also kind of eerie to be honest). The “screen of consciousness” starts looking like just one possible way to organize the field, corresponding to a particular kind of stable vortex configuration. But there are so many other possibilities! The path integral approach lets us understand how a completely “centerless” state could still be conscious – it’s just integrating over all possible perspectives simultaneously, without privileging any particular viewpoint.
This framework helps explain why 5-MeO-DMT can produce states of “pure consciousness” without content – when the field topology simplifies enough, the path integral becomes trivial. There’s literally nothing to distinguish one perspective from another. In a perfectly symmetrical manifold, all points of view are exactly the same. This ultimately ties in to the powerful valence effects of 5-MeO-DMT, seen through the lens of a field-theoretic version of the Symmetry Theory of Valence (Johnson 2016). We’re currently developing valence functions for field topologies, though we don’t yet have concrete results worth showing (but writeup about it forthcoming). Conversely, if this framework is accurate, then DMT’s complex topology creates many local extrema, each serving as a kind of perspectival anchor point, leading to the sensation of multiple observers or entities. This would be predicted to have generically highly mixed valence, with at times highly dissonant states and at times highly consonant states, yet always rich in internal divisions and complex symmetries rather than the “point of view collapse” characteristic of 5-MeO-DMT.
Our electromagnetic field visualizations make this particularly concrete. When we observe the magnetic field configurations in our simulations, we’re essentially seeing snapshots of the space over which these path integrals are computed. In the DMT-like states, the field is rich with vortices and anti-vortices – each one representing a potential perspective from which to “view” the field. The path integral must account for all possible paths through this complex topology, including paths that connect different vortices. This creates a kind of “quantum tunneling of perspective” (I know how this sounds, but bear with me) where consciousness can leap between different viewpoints, perhaps explaining the characteristically bizarre spatial experiences reported on DMT. In contrast, when we apply the 5-MeO-DMT-like kernel, we watch these vortices collapse and merge. The topology simplifies until there’s just one global structure – or sometimes none at all. At this point, the path integral becomes trivial because all paths through the field are essentially equivalent. There’s no longer any meaningful distinction between different perspectives because the field has achieved a kind of perfect symmetry.
Conclusion: A Network of Insights
This theoretical framework – connecting coupling kernels, field topology, and conscious experience – emerged from years of collaborative work and inspiration. While the specific insights about coupling kernels and their effects on field topology are my contributions, they stand atop a mountain of brilliant work by the extended QRI family.
I’m deeply grateful to Chris Percy for his rigorous development of these ideas, particularly in understanding their philosophical implications in the context of the current literature of consciousness studies, Michael Johnson for years of fruitful collaboration (and his great contribution to the field via the Symmetry Theory of Valence and formalization of Neural Annealing), as well as really helpful QRI advisors like Shamil Chandaria, Robin Carhart-Harris, and Luca Turin. Also special thanks to the great long-time doers in QRI like Hunter Meyer, Marcin Kowrygo, Margareta Wassinge and Anders Amelin (RIP). Cube Flipper’s phenomenological investigations of 5-MeO-DMT have been invaluable, as have the insights from Roger Thisdell, Wystan Bryan-Scott, Asher Arataki, and others. Everyone on the HEART team’s dedication to careful exploration has provided crucial empirical grounding for these theoretical developments.
I’m also excited about ongoing work with our academic collaborators (to be announced soon – we’re currently designing studies to test these ideas rigorously). In particular I want to thank Till Holzapfel for his awesome research and collaborations (and help with the QRI Amsterdam meetup!), Taru Hirvonen for her visual intuitions and work, Emil Hall for his amazing programming and conceptual development help, Symmetric Vision for his incredible visual work and intuitions, Ethan Kuntz for his insights on spectral graph theory, Scry for his retreat replications, and Marco Aqil for his ground-breaking research (and for giving a presentation at the recent Amsterdam meetup), and many more people who have recently been delightful and helpful for the mission (special shoutout to Alfredo Parra). This emerging research program promises to put these theoretical insights to empirical test, and we’re working at a team to bridge phenomenology and hard neuroscience. It’s happening! 
Also, none of this would have been possible without the broader QRI community and its supporters – a group of fearless consciousness researchers willing to take both mathematical rigor and subjective experience seriously. Together, we’re building a new science of consciousness that respects both the precision of physics and the richness of lived experience.
The path ahead is clear (well, at least in my head): we need to develop more sophisticated simulations of field topology, particularly in three dimensions, and devise clever ways to test these ideas experimentally through psychophysics and microphenomenology. The coupling kernel paradigm offers a concrete mathematical handle on consciousness – one that might let us not just understand but eventually engineer specific states of consciousness. It’s an exciting time to be working on this hard problem!
Thanks for coming along on this wild ride through field topology, psychedelic states, and the mathematics of consciousness. Stay tuned – there’s much more to come!
– Andrés 
Tags
Consciousness, Psychedelic, Coupling Kernels, Field Topology, Neuroscience, Phenomenology, BaaNLOC